Start improving with Life QI today
Full access to all Life QI features and a support team excited to help you. Quality improvement has never been easier.

Organisation already using Life QI?
Sign-up

Published on 21 November 2022 at 15:45
by Reka Toth

Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles are a four-step improvement tool used by a wide range of industries to test small changes quickly and cost effectively.
In this article we’ll look at the first, planning phase of the process. It’s the foundation of the whole PDSA cycle, so we highly recommend dedicating enough time to refine your idea and create a plan around it.
Life QI is a simple online system which enables improvement teams to plan their PDSA cycles and change settings in real time, anywhere and anytime. You can access the PDSA cycle functionality in the dedicated PDSA area of your Life QI project.
After giving a title to your PDSA cycle, you can start to set your aim, map out the plan of how to test the idea, form a team, make predictions, and develop a plan to measure the results.
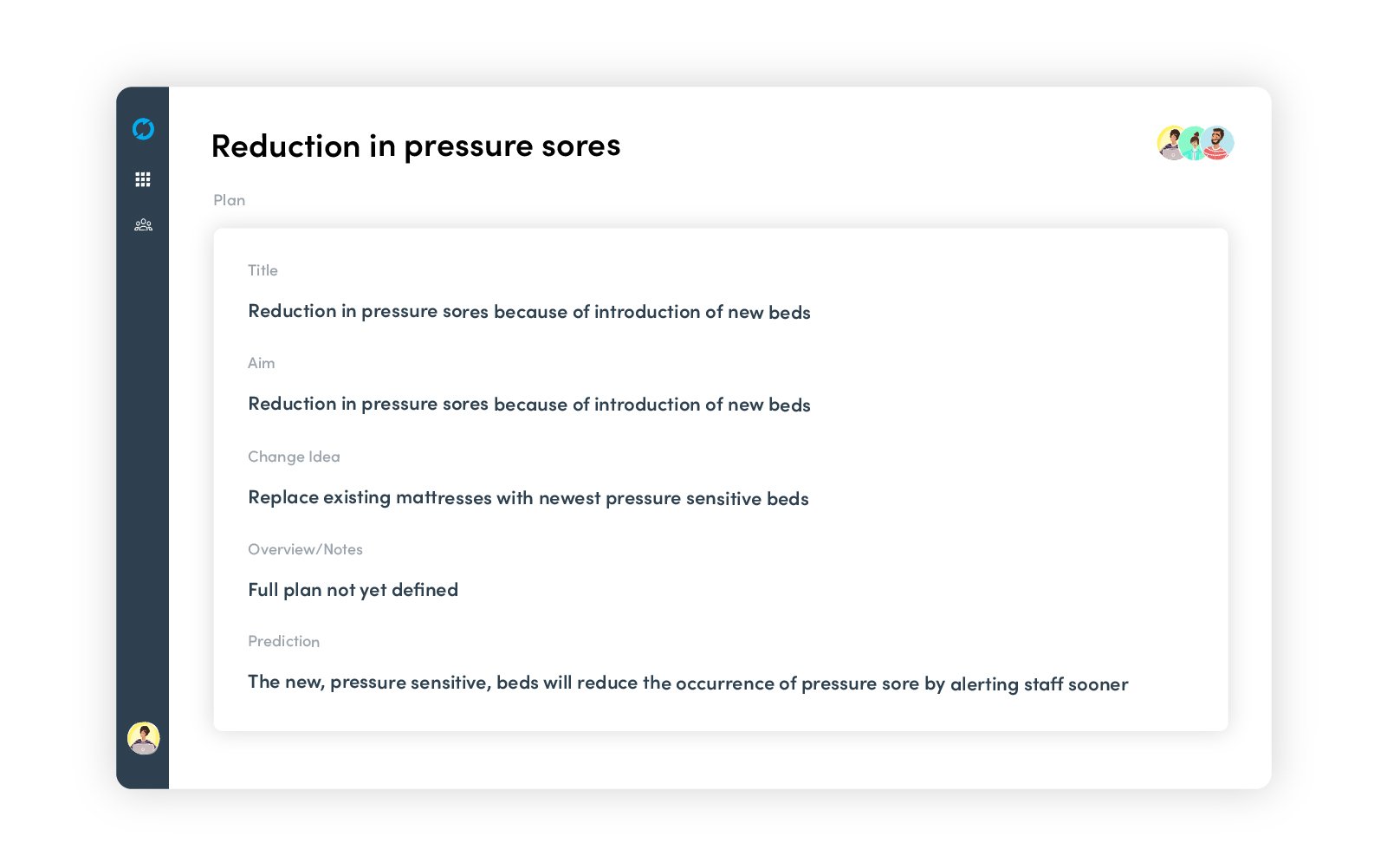
Figure 1: Planning a PDSA in Life QI
The purpose of this phase is to investigate the current situation, fully understand the nature of any problem to be solved, and to develop potential solutions to the problem that will be tested.
First of all, you have to develop an aim statement. PDSAs are about trying small ideas quickly and iterate as needed. Do the initial PDSA on the smallest scale possible. For example, test your idea on one patient, on one staff member, or reduce the length of the test from a month to a week or a day.
This enables you to test the idea in a short time and move quickly from cycle to cycle. When writing your aim, don’t forget about choosing a SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Timebound) goal. We suggest answering the following questions when thinking about the aim statement:
Your aim statement is a key component of the entire improvement process. It’s essential to quantify the improvement you are looking to achieve. You might find it necessary to revisit and refine it as you move through the planning phase.
To have all the information regarding your improvement project connected with each other, you need to assign the change idea you decided to test. It’s a concise statement of what you plan to do in this testing. If you have a driver diagram created in Life QI, you only need to choose the relevant change idea from the dropdown menu.
We encourage the implementation of small-scale ideas that can be trialed quickly, with lower cost, and with minimal disruption in your regular processes.
Related articles:
How to create a driver diagram with primary and secondary drivers and change ideas
10 easy ways to create great change ideas
By providing detailed instructions in the planning stage, you can make sure that your teams successfully execute the test. It makes easier the analysis later in the progress to identify the pain points that can be applied to the next cycle.
Ensure clear directions by assigning tasks to specific team members. It's crucial to make sure that everyone knows who is responsible for which task.
You can simply do it on the Task tab:
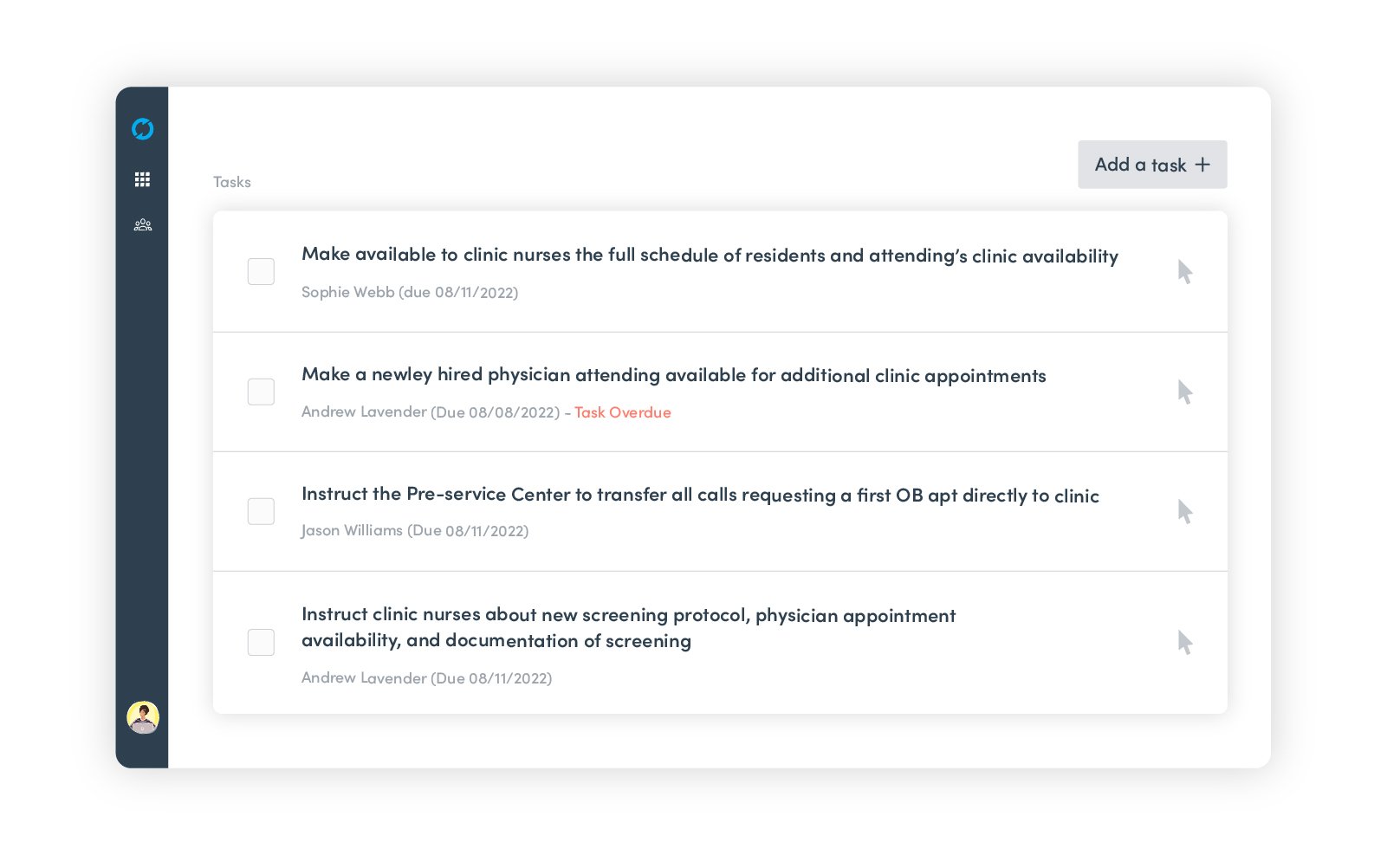
Figure 2: Add tasks to a PDSA cycle in Life QI
Life QI will automatically list the tasks in order of the date that they need to be completed by, starting with the closest deadline first.
By ticking the checkbox next to the task once it’s completed you help other users on the same project to get informed of the progress you made.
In this section you can add action plan for your PDSA cycle - the steps that you are going to take in order to achieve your aim.
The details of this plan should include all aspects of the method to test the change was an improvement. Include information about what data will be collected, how frequently data are collected, who collects the data, how they are documented, the timeline, and how results will be analysed.
Baseline data that describe the current state are critical to get a full understanding of the existing process. This data serves as a foundation to quantifiably measure the success of your PDSA cycle. The data may address, for example, time, people, space, cost, number of steps, adverse events, and customer satisfaction.
There are many types of charts to choose from depending on the type of data you want to measure, including run charts and different types of control charts. It’s really important that the data collected must be aligned with the measures listed in the aim statement.
Related article:
Pick the right SPC Chart every time
To link your PDSA to one or more measures, what you only need to do is to select it from the dropdown menu. You can also add an annotation to the same chart by clicking on a data point and choosing the relevant PDSA from the list.
Once you have decided how you are going to evaluate the impact of the change and linked to the relevant measure(s), you should make a hypothesis of what you expect to achieve as a result of your intervention.
A numerical prediction can help you and your team better predict the size of the change needed, and identify the resources needed to support it.
Prediction is a useful prompt to think about what might go wrong during the test or what might prevent the test from being successful. This can sometimes lead to the plan being changed thanks to mitigate the risks identified at the prediction step. This kind of robust preparation is needed to give each test the best chance of success.
It will also have a huge importance in the Study phase of your PDSA cycle when you want to evaluate its results and compare what you achieved to the prediction you made or with the results between different PDSA cycles.
Here are a couple of examples of how you can complete the planning part of the PDSA tool in Life QI.
Title: Provide patients with more info on pressure sores
Aim: Provide patients with more info on pressure sores will reduce the likelihood of them getting sores
Change idea: Include pressure sore prevention information in admission material
Overview/Notes: Source additional pressure sore information and pass to the team for inclusion in admission packs.
Prediction: A small percentage of patients will be more aware and conscious of pressure sore prevention measures.
Linked measures: Proportion of patients suffering from pressure sores (P Chart)
Title: Increase students performing at proficient or above in math
Aim: The percentage of students performing at proficient or above in math will increase by 10% in the next 3 months.
Change idea: Teachers implement conversation protocol to promote active listening.
Overview/Notes: 1 math teacher in 1 class will test the idea in the next 3 months. Mr Matthews will implement the protocol in his Year 11 Set 1 maths class, starting 15th September. Mr Matthews will record the students’ grades on a weekly basis after each in-class test.
Prediction: Unlikely to see much change in grades from baseline level in the first month but expect grades to pick up in month 2 and further in month 3. Expect a small cohort of students to not respond to protocol and grades remain largely at the same level.
Linked measures: Percentage of students performing at proficient or above in math (P chart)
As you can see Life QI offers an all-in-one platform solution to plan out your PDSA cycle. Spending adequate time to the planning phase of the PDSA cycle is imperative to have a smooth and meaningful quality improvement process.
Full access to all Life QI features and a support team excited to help you. Quality improvement has never been easier.

Organisation already using Life QI?
Sign-up