Start improving with Life QI today
Full access to all Life QI features and a support team excited to help you. Quality improvement has never been easier.

Organisation already using Life QI?
Sign-up
You are in good company If you are interested in running a Quality Improvement (QI) Collaborative!
Healthcare settings have been using collaboratives to improve quality of care, enhance patient safety and drive organisational change since the mid-1990s, when they became popular via the Institute for Healthcare Improvement’s (IHI) Breakthrough Series model.
QI Collaboratives are groups of people from different units or organisations who work together in a structured way and share learning and experience in order to create more efficient services. Collaboratives are generally set up to enhance patient safety, quality and efficiency of care.
To quote from the BMJ article ‘Quality collaboratives: lessons from research’: “A collaborative brings together groups of practitioners from different healthcare organisations to work in a structured way to improve one aspect of the quality of their service.”
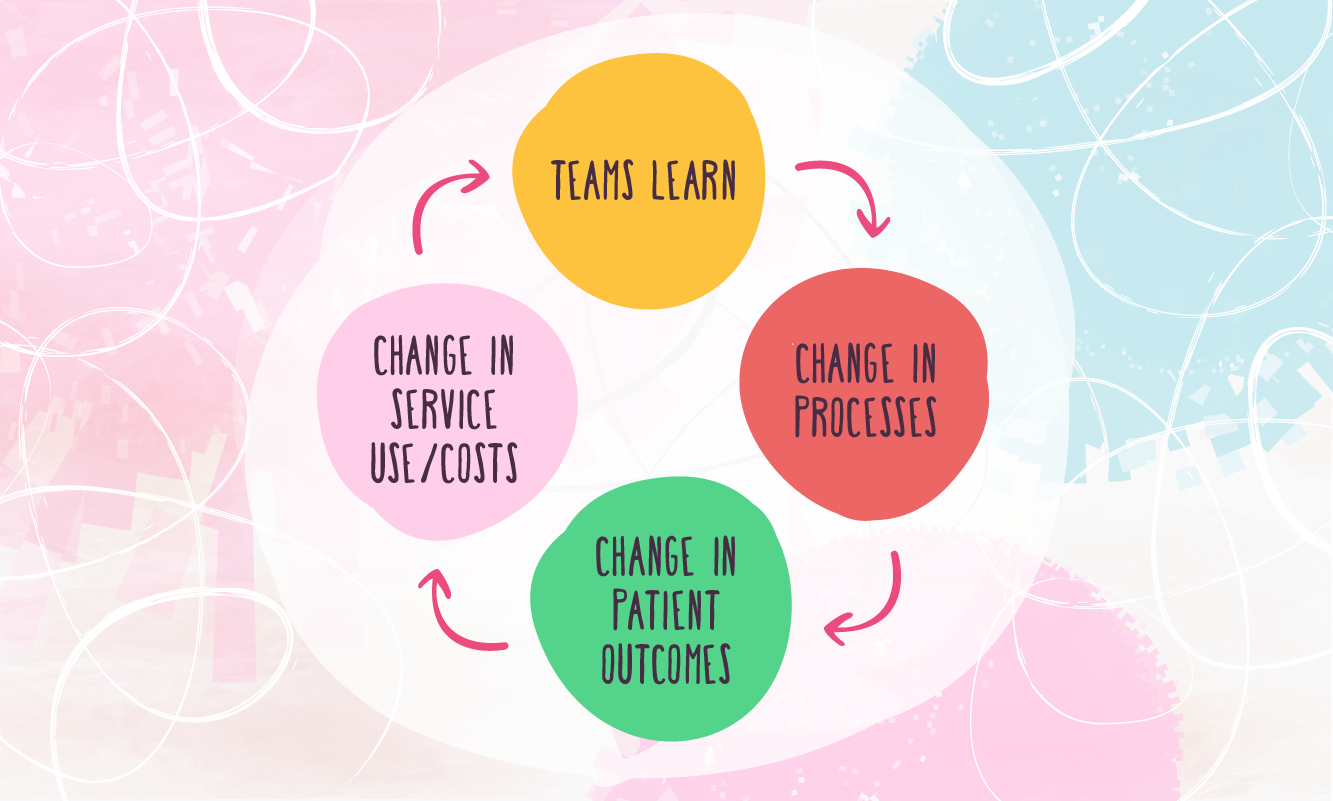
Collaboratives often use the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) approach to make incremental changes, with teams meeting up during a period of 6 – 15 months for face to face meetings and communicating on conference calls, while benchmarking progress and monitoring. Teams in such collaboratives have achieved dramatic results, including reducing waiting times by 50 percent, reducing worker absenteeism by 25 percent, reducing ICU costs by 25 percent, and reducing hospitalisations for patients with congestive heart failure by 50 percent.
If you want to run a successful improvement collaborative to encourage transformational change, patient safety and quality improvement – it’s really important to set it up it correctly, right from the start. There are a good number of collaboratives already established in the UK which have improved health care quality, so it may be a good idea to familiarise yourself with their experiences in the first instance. For example, East London Foundation Trust (EFLT) have done some great patient safety work in collaborative format.
The Health Foundation’s report, Improvement collaboratives in Healthcare, concludes that collaboratives are more likely to be effective if they follow a series of rules in approach:
This should be the first step in your collaborative journey. Your area for the collaborative’s focus might be something that you feel needs immediate attention or it might be an idea to focus on topics where good practice is already established. The Health Foundation suggest you focus on topics where there is ‘established good practice and a large gap between current and ideal performance’.
This is a really important consideration before you start your collaborative. First consider the organisations (hospitals etc.) that you are trying to engage as part of the initiative. This will dictate the scale and number of participants involved. Next up, think about the types of people that will need to be involved - it would be wise to choose experts in your focus area. You should also choose people who will get things done. Once you’ve established your team, you will need to gain ‘buy in’ from senior leaders, who will motivate others to participate. You should also think about including people across disciplines so you have a multi-disciplinary team – this will lead to better ideas with a broader scope of expertise.
Goal setting is really important from the outset, and it is recommended that you set clear goals that participants can be accountable for. In its report, the Health Foundation suggests that you start with presenting a ‘theory of change’ so measurements can be made, and so there is a clear link between activities and the outcome you want. Effective communications channels are also vital to keeping momentum.
This is a really important element. If you want to succeed in your collaborative, you need to have a sound IT infrastructure and measurement tools or benchmarking tools. You could also consider using support from experts to help make your transformation journey easier – for example Life QI’s software provides a range of support for those taking part in collaboratives – including a central hub where users can track and measure their quality collaborative work.
Successful collaboration between disparate teams can be a real challenge. The success of an improvement collaborative is often dictated by the ability and willingness of teams to share learnings and successes. Consider how you will facilitate this.
First up, you probably need a kick off meeting - this is the launch of the collaborative and your stage to get leaders, champions, sore team and participants together to ensure everyone is on the same page. It is a chance to communicate the value of the initiative and to present the plan and practicalities of the work. It might also be an opportunity to collect ideas from the community. This first session often sets the tone for the rest of the initiative so it is worth planning carefully.
Secondly, you are probably going to want some ongoing activities to engage participants, provide a point of reference and to facilitate sharing between teams. This could include monthly calls/learning sessions, face-to-face meetings, webinars etc.
It’s great that you have chosen to run a QI Collaborative - there are lots of real QI success stories where teams have used the collaborative model.
Before you start: do your research, think about the tools that could support you. Collaborative working doesn't have to be a costly affair. Life QI helps large-scale collaborations successfully work on improvement projects remotely, driving down travel costs.
There are also some great real-world examples: ELFT launched their quality improvement programme in 2014 with a specific vision, to: 'Improve the quality of life of all the people we serve'. ELFT uses the Life QI system to track improvement and work progress.
The Healthcare Foundation report on Collaboration in Health Care states: “Qualitatively, collaborative teams are reported to demonstrate improved sharing of evidence-based practices between professions, improved decision-making, and increased innovation. Quantitatively, collaborative team-work may lead to reduced length of hospital stay, improved compliance with standards of drug prescription, improved quality audit results, and improved symptom and psychosocial management.”
Full access to all Life QI features and a support team excited to help you. Quality improvement has never been easier.

Organisation already using Life QI?
Sign-up